When searching to improve business efficiency and processes, oftentimes logistics companies turn to Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) solutions. The two main types of RFID are passive and active. Both systems have advantages and disadvantages. So, which is the ideal solution? Well, it depends on the company’s use case. Let us take a closer look at this question.
What is Passive RFID?
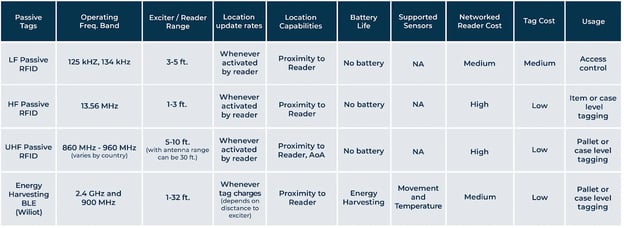
Passive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. The two main parts of a passive RFID system are the reader (or interrogator) and the tag. Each tag has two main components, the antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). Once a reader sends a signal to a tag, that signal or energy moves from the tag's antenna to the IC. The IC converts that energy into a radio frequency wave, which is sent back to the interrogation zone or RFID reader for interpretation.
Fun Fact: Passive RFID tags are not the same as barcodes or QR codes.
What is Active RFID?
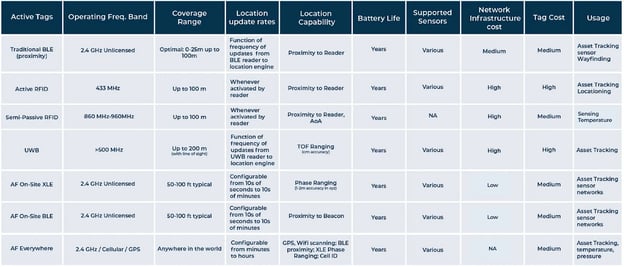
Active RFID is mainly different from passive because it involves being powered internally through a battery. Because active tags do not need a reader to energize them, they can continuously broadcast their signal. Any reader that passes by can identify the tag by receiving its radio waves.
Some active tags do not transmit data continuously because it drains the battery. Most readers can transmit an interrogation signal to wake up the tag. This sends a unique identification signal back to the reader via the antenna. With either method, the reader transfers the information to the system, where it is analyzed.
Three Different Types of Active RFID Tags
Transponders – In a system that uses an active transponder tag, the reader (like passive systems) will send a signal first, and then the active transponder will send a signal back with the relevant information. Transponder tags are very efficient because they conserve battery life when the tag is out of range of the reader.
Beacons – In a system that uses an active beacon tag, the tag will not wait to hear the reader’s signal. Instead, the tag can send out its specific information every 3 - 5 seconds. Active tag beacons can be read hundreds of meters away, but to conserve battery life, they may be set to a lower transmit power to reach around 100 meters read range.
Intelligent RFID - Intelligent RFID is a hybrid of sorts that combines beaconing and transponding. Intelligent active RFID tags are designed to wake up at established intervals, scanning their environment for nearby fixed reference point beacons, which they use to calculate their locations (the “intelligent” function). Then the tags send this data back to the reader.
Differences Between Passive and Active RFID Tags
Both passive and active tags will have some real-time location capabilities, but the use case will determine whether or not passive or active tags are the right choice. The main difference between passive and active RFID is the power source. Passive tags must have a reader to be powered, while active tags are powered with a battery. The ability to be powered internally is more feasible for asset tracking because the tags do not need to be as close to the reader or interrogator. This factor also affects the ranges that active and passive tags can be used. Being powered internally means active tags can be used when tracking will be done at greater distances.
The beacon system that is available on active tags also means the tag will initiate the communication, which is important when tracking assets at further distances that need to be monitored frequently. The location capabilities for passive tags are reliant on the proximity to the reader. This means that the reader initiates the signal when near the passive tag. The size of tags also differs and because passive tags do not have a battery they are much smaller. Active tags on the other hand are normally the size of a smartphone. Active tags can be used in more harsh environments, while passive tags are normally used in indoor environments like a warehouse or factory. The benefit of passive tags not having a battery is that there is no need to worry about replacing the power source and the tags can essentially last forever. Also, these tags are less expensive making it easier for a company to purchase many of them.
However, it is most practical to use a small number of passive tags in a restricted geographic area. This is because it would increase the number of readers needed. Active tags do have batteries, and these batteries will of course need to be replaced eventually, normally within 3-7 years.
Increase Your ROI by Investing in AirFinder Everywhere
- Loss Prevention. Reduce the amount of loss that occurs during the supply chain process
- Location Coverage. AirFinder Everywhere uses a combination of GPS, Cellular, and WiFi to determine location everywhere
- Security Alerts. Know when a delay in shipment has occurred so the problem
can be addressed immediately.
Logistics
The logistics industry involves the entire operation that takes place when resources are purchased, stored, and delivered to the end-user. The coordination of activities in the logistics process is vital to the success of an organization and to ensure that the client is receiving a quality product in a timely manner. A tracking system is necessary to increase visibility. This way, assets can be tracked in the inventory and the transportation process. RTLS is the solution to this issue and can be solved with RFID tags. There are various questions to consider when determining if active or passive tags are the better option. If the items are indoor or outdoor, the range needed to track, and the frequency of location updates are all important things to consider before choosing.
Due to their location capabilities, passive tags would be better to be used indoors. Also, using passive tags at scale is unrealistic due to the need for a large number of readers. Active tags can be used at a longer range making them better for tracking during transportation. Active tags are powered internally, so there is no need to worry about having a reader close by. Active tags can hold up better in outdoor environments and inclement weather. The use case will determine if active or passive tags would be better, but active tags capabilities for various use cases. Whether the use case is asset tracking, WIP tracking, loss prevention, or process monitoring, RFID tags can increase visibility.
Use Cases of RFID
Passive RFID tags are lower priced and small making them applicable to a variety of situations. However, these use cases are limited to indoor situations due to their lower range and needing to be within a certain proximity of the reader. A company can use passive RFID for inventory or WIP tracking. Also, these tags are useful when looking to prevent theft and loss of assets. Passive tags can also be used in access control. With access control, a company can monitor employees with RFID-powered ID badges. This increases security and can give control through long-range access. For active RFID tags, there are far more use cases that involve the logistics industry.
Being able to track items when they are in transit is a crucial aspect of the logistics industry. With active tags, a tagged object can be pinpointed and the user can know the exact location. An organization can utilize this technology to track assets that are within a facility or being transported. Overall, a logistics company would benefit from using active RFID tags as opposed to passive RFID tags. However, other important considerations must be made. There are other options besides RFID that can be used in the logistics industry such as BLE, XLE, Wi-FI, and GPS technology.
AirFinder Everywhere
An alternative solution to RFID tracking tags is AirFinder Everywhere. With the AirFinder Everywhere platform by Link Labs, assets can be seamlessly tracked indoors and outdoors. This system can be used in a variety of industries, including; logistics, equipment rental, maintenance, and inventory control. There are four technologies used to track items, Cell Tower ID, WIFI Lookup, GPS, and the AirfInder OnSite Network. Each of these technologies that are used vary depending on the location of the items and the range. This varies from passive and active RFID tags that use their own signal to transmit or wait for a signal from the beacon or transponder. Using these technologies also saves battery life and alerts can be set depending on various factors. Updates can be sent depending on the movement or location of the tag. The four tags offered by Link Labs on this platform are the Supertag Pro, Supertag Plus, and the rechargeable Supertag. Overall, AirFinder Everywhere is a great solution that does not use RFID technology. If your organization is involved in logistics and is seeking to track assets, click here to learn more about what Link Labs has to offer and the background behind our technology.





