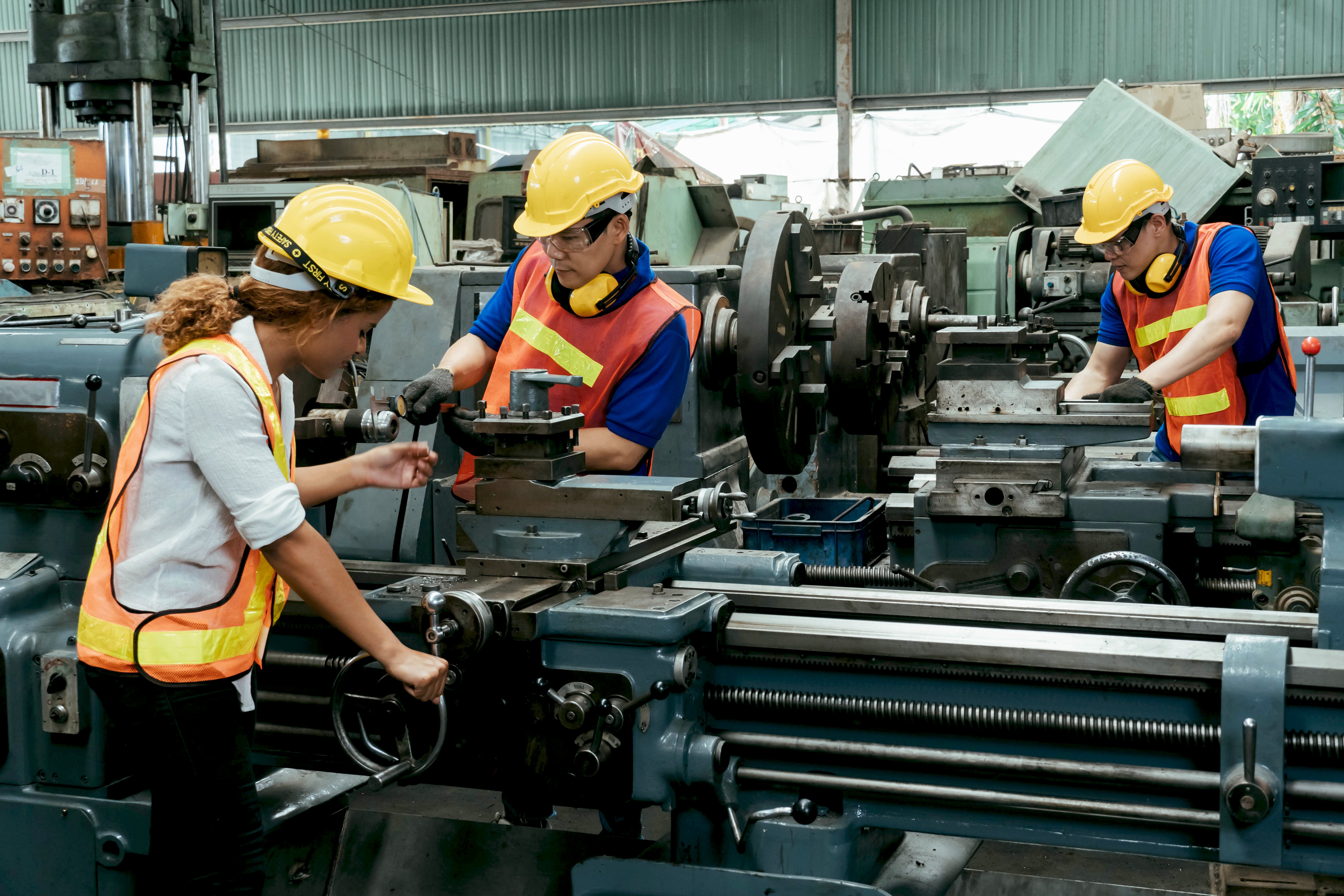
How RFID Works for Asset Tracking
RFID location tracking uses Internet of Things (IoT) technology to identify assets like inventory, equipment, or even people. New versions are continually being developed to improve their capabilities.
Through various means of RFID asset management, such as active and passive, users have the power to select the option that works best for them.
Frequency-based technology
RFID is a method of sending or receiving messages from tags for asset tracking using specific frequencies. RFID doesn’t require the continuous transmission of information.
Passive RFID
RFID tracking systems are battery-free processes whereby a reader sends out a radio frequency signal that essentially “wakes up” the tag. A great example of RFID technology use is the passing through of toll booths.
Active RFID
Active RFID leverages batteries in tags and often works in concert with Bluetooth or Bluetooth Low Energy (LE), though other options are available. These systems are battery-powered sensors that connect to various access points throughout an area (like a building) and transfer data to the cloud.
Active RFID Range
Active RFID tool tracking range can be greater than 100 feet between the RFID tag and reader. This allows Active RFID systems to scale quickly since you could potentially cover 10,000 square feet with one Active RFID reader and a few reference points.









.webp?width=1276&height=1650&name=The-7-Costs-of-RFID-Whitepaper-Thumbnail%20(1).webp)











